What is Graphic Designing?
Graphic designing is a creative discipline that involves combining visual elements, typography, and imagery to communicate messages or ideas. It is the art and practice of planning, projecting, and arranging visual content to convey information, evoke emotions, or promote a specific concept or product.
Attractive designs and logos capture everyone’s attention. It helps in fast branding of products leaving an image memory for the audience.
If you are the one who is planning for a brand start or a website launch, this is the time you should understand what graphic designing is. Because it makes it easy for you to spread your idea to the masses.
Read further to know what graphic design basics.
What is Graphic Design?
Graphic design is using visuals as the medium to communicate your idea.
- Graphic design encompasses various mediums, including print materials, digital media, advertisements, websites, logos, packaging, and more.
- Graphic designers use design principles and techniques to create appealing and compelling compositions. They consider color theory, typography, layout, balance, hierarchy, and imagery to craft visually pleasing designs and convey the intended message. They often work with design software tools like Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator, and InDesign to create their designs.
- The main goal of graphic design is to communicate a message or tell a story visually, compellingly, and engagingly.
- It involves understanding the target audience, the purpose of the design, and the desired outcome.
- Graphic designers play a crucial role in branding, marketing, and communication strategies, as they help businesses and individuals visually represent their identity, products, or services to the world.
Also Read: What is UI/UX Design?
Types of Graphic Design
There are several types of disciplines within the field of graphic design. Here are some of the main types:
Visual Identity/Brand Design
This involves creating the visual elements that represent a brand, such as logos, typography, color palettes, and overall brand guidelines.
When creating a visual identity or brand design, here are some tips to consider:
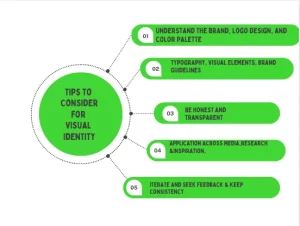
- Understand the Brand: Know the brand’s values, personality, target audience, and unique selling points.
- Logo Design: Create a memorable logo that reflects the brand’s essence. Make sure it’s simple, versatile, and looks good in different sizes and uses.
- Color Palette: Pick colors that match the brand’s personality and evoke the right emotions. Think about how colors work together and aim for a consistent color scheme.
- Typography: Choose readable fonts that suit the brand. Create a hierarchy of fonts for different uses, like headings, subheadings, and body text.
- Visual Elements: Design icons, patterns, or illustrations that reinforce the brand’s identity and style.
- Brand Guidelines: Make a clear set of rules for using the brand’s visual elements. Include info on logo placement, colors, fonts, and design rules.
- Application Across Media: Think about how the brand’s look will work in different places, like online, in print, on packages, and signs. Make sure it adapts well while staying recognizable.
- Research and Inspiration: Stay up-to-date with design trends and look at successful brand designs for ideas. Aim for a unique and timeless design.
- Iterate and Seek Feedback: Keep refining your designs based on client, colleague, or target audience feedback.
- Consistency is Key: Make sure the brand’s visuals stay the same across all places where it’s seen, like websites, social media, ads, packaging, and more. This builds recognition and reinforces the brand’s identity.
Print Design
This includes designing printed materials such as brochures, posters, business cards, packaging, magazines, and newspapers. While preparing the print design, these are the things that you should take care of:
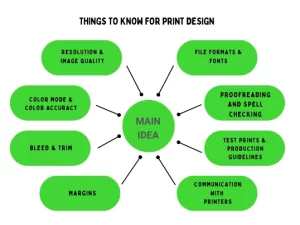
- Resolution and Image Quality: Use high-quality images and graphics (at least 300 dpi) to keep them sharp and clear when printed. Low-quality images may look blurry or pixelated on paper.
- Color Mode and Color Accuracy: Design using CMYK colors for print. Ensure all images and graphics are in CMYK to get the right colors. Use tools to keep colors consistent between your screen and the printed version.
- Bleed and Trim: Include extra space around the edges of your design (bleed) to prevent white borders after trimming. Make sure not to put important stuff in the bleed area.
- Margins and Safe Zones: Keep important text, logos, and design elements away from the edges to prevent them from being cut off during trimming. Leave some space inside the page for critical content.
- File Formats and Compatibility: Save your designs in PDF or TIFF formats to keep the quality and colors intact and ensure they work with different printers.
- Typography and Fonts: Use easy-to-read fonts for print and stick to a few fonts to keep things looking consistent. Make sure to embed or outline fonts to appear correctly on different devices.
- Proofreading and Spell Checking: Carefully check for your designs’ spelling, grammar, and typing errors. It’s a good idea to have others review it, too.
- Print Production Guidelines: Understand the rules for your printing method. Different types of printing may have specific rules about colors, file formats, and quality.
- Test Prints: Before printing many copies, make a few test prints to check colors, layout, and overall appearance. Fix any problems before you print a large batch.
- Communication with Printers: Talk to the printer to ensure they can handle your design. Ask questions and get their advice to avoid problems during printing.
Example of print design includes one from Nike. Nike’s print ads are known for their bold and eye-catching visuals. They often feature athletes in action, using dynamic typography and vibrant colors to create a sense of energy and excitement.
Web Design
Web designers create layouts and graphics for websites, focusing on user experience, functionality, and aesthetics.
Here are some tips for web design in graphic designing :
- Understand the target audience and design with their preferences and needs in mind.
- Keep the layout clean, organized, and easy to navigate for a seamless user experience.
- Ensure the website is responsive and mobile-friendly, adapting well to different screen sizes and devices.
- Use a consistent color scheme and typography throughout the website for visual coherence.
- Optimize images and graphics for the web to maintain fast loading times.
- Pay attention to readability by using appropriate font sizes, line spacing, and contrast between text and background.
- Incorporate clear call-to-action buttons and intuitive navigation menus for easy user interaction.
- Utilize white space strategically to enhance visual hierarchy and make the content more digestible.
- Implement user-friendly forms and input fields with clear instructions and validation messages.
- Prioritize accessibility by following WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines) standards for inclusive design.
- Test the website across browsers and devices to ensure compatibility and consistent performance.
- Regularly update and maintain the website to fix bugs, improve functionality, and keep the design current.
- Incorporate SEO (Search Engine Optimisation) best practices to improve the website’s visibility in search engine results.
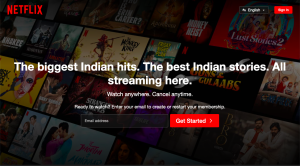
Source: Netflix.com
Example of web design can be the website of Netflix is an excellent example of how graphics can create a visually appealing and engaging user experience. The homepage features a large, high-quality image of a popular Netflix show, immediately capturing the user’s attention. The idea is accompanied by a short, attention-grabbing headline and a clear call to action.
User Interface Design
UI designers focus on designing interfaces for digital products, including websites, applications, and software, to ensure a smooth and intuitive user experience.
These are some quick tips to keep in mind for UI designing:
- Prioritize User-Focused Design: Design with the end user in mind, considering their goals, needs, and behaviors.
- Maintain Consistency: Ensure consistency in visual elements, such as colors, typography, and icons, to provide a unified and intuitive user experience.
- Keep it Simple: Strive for simplicity in design, avoiding unnecessary clutter or complexity that can confuse or overwhelm users.
- Provide Clear Navigation: Use intuitive navigation patterns, such as menus, breadcrumbs, or a well-structured information architecture, to help users quickly navigate the interface.
- Use Visual Hierarchy: Employ visual cues, such as size, color, and contrast, to establish a clear information hierarchy and guide users’ attention to important elements.
- Utilize Whitespace: Use whitespace strategically to create breathing room and improve readability, allowing users to focus on the essential content and interactions.
- Enhance Readability: Choose legible fonts, appropriate font sizes, and suitable line spacing to ensure text is easily readable across different devices and screen sizes.
- Focus on Intuitive Interactions: Design interactions that feel natural and predictable to users, minimizing the need for instruction or tutorials.
- Provide Feedback: Offer visual feedback, such as animations or micro-interactions, to inform users about their actions and system responses, enhancing usability and engagement.
- Conduct Usability Testing: Regularly test your UI design with real users to identify pain points, gather feedback, and make iterative improvements.
- Consider Accessibility: Design with accessibility in mind, ensuring the interface is usable for people with disabilities and compliant with accessibility standards.
- Iterate and Iterate: UI design is an iterative process, so continuously gather user feedback, iterate on your designs, and refine the interface based on real-world usage and user needs.
One example of excellent graphics in UI design could be Spotify uses a vibrant color palette to create a visually appealing and engaging user experience.
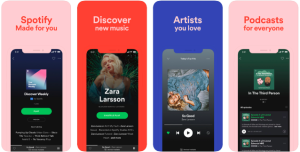
Source: Careerfoundary
The colors differentiate between different types of content, such as playlists, albums, and artists. They are also used to create a sense of excitement and energy.
User Experience (UX) Design
UX designers enhance the overall user experience by considering usability, accessibility, and user interactions with digital products or services.
- Understand User Needs: Conduct research to deeply understand your target users’ needs, goals, and behaviors.
- Simplify and Streamline: Strive for simplicity and efficiency in the user journey, removing unnecessary steps or complexities.
- Design for Task Completion: Ensure users can easily and successfully complete tasks by providing clear instructions and logical workflows.
- Prioritize Content: Present relevant and valuable content prominently, making it easy for users to find and engage with.
- Optimize Performance: Focus on fast loading times and smooth interactions to prevent user frustration.
- Provide Feedback: Offer real-time feedback and status updates to keep users informed and engaged during their interactions.
- Foster Consistency: Create a consistent experience across different touchpoints and interactions to reduce cognitive load.
- Test and Iterate: Continuously test your design with real users, gather feedback, and make iterative improvements based on their insights.
- Incorporate User-Centric Design: Involve users throughout the design process, soliciting their feedback and incorporating their insights into the decision-making process.
- Prioritize Accessibility: Ensure your design is inclusive and accessible to all users, considering factors such as color contrast, readability, and support for assistive technologies.
- Embrace Visual Hierarchy: Use visual cues to prioritize and guide users’ attention to the most important elements and information.
- Foster Emotional Connection: Design experiences that evoke positive emotions, creating a memorable and engaging user experience.
Advertising Design
Advertising designers create visuals for various advertising campaigns across different media platforms, such as print ads, online banners, billboards, and social media ads.
For advertising design this is what you can keep in mind:
- Know Your Target Audience: Understand your target audience’s demographics, preferences, and behaviors to tailor your design to their interests and motivations.
- Grab Attention: Create a visually striking and attention-grabbing design that stands out from the competition and immediately captures the viewer’s interest.
- Clear Message: Craft a concise and compelling message that clearly communicates the unique selling proposition or key benefits of the advertised product or service.
- Strong Visuals: Use high-quality images, illustrations, or graphics relevant to the message and evoke the desired emotions or associations.
- Call to Action: Incorporate a clear and persuasive call to action that prompts the viewer to take the desired next step, such as purchasing, visiting a website, or contacting the company.
- Consistent Branding: Maintain consistency with the brand’s visual identity, including the logo, color palette, typography, and overall style, to reinforce brand recognition and coherence.
- Test and Refine: Test different versions of your design to see which resonates best with your target audience. Collect feedback and data to make informed refinements and improve the effectiveness of your advertising.
Graphics are often used to attract attention to an advertisement. This can be done using bright colors, bold images, or eye-catching typography.

Source: Vogue
For example, a perfume ad might use a close-up of a woman’s face with her eyes closed and lips slightly parted. The image would be accompanied by an intense fragrance name and a tagline that evokes sensuality.
Motion Graphics Design
Motion designers combine graphic design elements with animation techniques to create visually engaging motion graphics, typically used in videos, presentations, and digital advertisements.
For motion graphics design, these are the things that you can take care of:
- Plan and Storyboard: Begin by planning and storyboarding your motion graphic design. Outline the key messages, transitions, and visual elements to ensure a cohesive and well-structured animation.
- Focus on Storytelling: Use motion graphics to tell a compelling story or convey information in a visually engaging and dynamic way. Think about the narrative arc and how each element contributes to the storytelling.
- Keep it Concise: Motion graphics often convey information quickly and succinctly. Keep your animations concise and avoid overcrowding the screen with excessive details.
- Use Visual Hierarchy: Apply visual hierarchy principles to guide viewers’ attention and emphasize important information. Utilize size, color, motion, and other visual elements to establish a clear hierarchy within your animation.
- Enhance with Sound: Consider incorporating sound effects, background music, or voiceovers to enhance the overall impact of your motion graphic design. Ensure the audio elements align with the visuals and complement the intended message.
- Optimize for Different Platforms: Remember the platforms or devices on which your motion graphics will be viewed. Optimize the design and file format to ensure smooth playback and compatibility across different devices and platforms.
- Iterate and Seek Feedback: Motion graphic design benefits from iteration and feedback like any design process. Regularly review your work, gather feedback from peers or clients, and make necessary refinements to improve the quality and impact of your animation.
Environmental/ Experiential Design
This design involves creating graphics for physical spaces, such as signage, wayfinding systems, exhibition displays, and environmental branding.
These are the things you can keep in mind for developing experiential designs:
- Define the Objectives: Clearly define the objectives and goals of the experiential design. Understand what you want to achieve and what kind of experience you want to create for your audience.
- Know Your Audience: Gain a deep understanding of your target audience’s preferences, needs, and behaviors. Tailor the experiential design to resonate with their interests and motivations.
- Immersive Experience: Create an immersive and memorable experience that engages the senses and captures the audience’s attention. Incorporate elements like interactive technology, multimedia, sensory cues, and spatial design to enhance the experience.
- Seamless Journey: Design a seamless and well-structured journey for participants, ensuring that every touchpoint contributes to the overall experience. Pay attention to the flow, transitions, and pacing to maintain engagement and coherence throughout the experience.
- Foster Emotional Connection: Craft experiences that evoke emotions and create a personal connection with the audience. Consider how you can trigger positive emotions, such as joy, surprise, or inspiration, to leave a lasting impact.
- Measure and Adapt: Implement mechanisms to measure the effectiveness of the experiential design, such as surveys, feedback, or data analytics. Use the insights gained to make iterative improvements and adapt the experience based on audience responses.
The Museum of Ice Cream in New York City is an excellent example of experiential design.

Source: Museum of Ice Cream
The museum is filled with interactive exhibits that allow visitors to learn about ice cream’s history and create their own ice cream creations. The displays are designed to be visually appealing and engaging, creating excitement and fun for visitors.
Illustration
Illustrators specialize in creating visual representations, often hand-drawn or digitally rendered, for various purposes like books, magazines, packaging, and advertising.
These are the pointers that can help you create impressive illustrations:
- Understand the Brief: Begin by thoroughly understanding the purpose and requirements of the illustration. Clarify the subject matter, style preferences, and any specific guidelines provided.
- Research and Gather Inspiration: Conduct research to gather inspiration and references related to your chosen subject or style. Explore sources like books, websites, or art galleries to expand your creative ideas.
- Sketch and Experiment: Start with rough sketches to explore various compositions, poses, and perspectives. Experiment with different concepts and layouts to find the best approach before moving on to the final illustration.
- Choose Suitable Tools and Mediums: Select the appropriate tools and mediums that align with your vision and intended style. This can include traditional mediums like pencils, ink, or paints and digital devices like graphic tablets or illustration software.
- Focus on Composition and Balance: Pay attention to the composition and balance of the illustration. Consider elements such as focal points, negative space, and visual flow to create a pleasing and harmonious composition.
- Add Detail and Polish: Once the overall structure is in place, add finer details, textures, and shading to enhance the depth and visual appeal of the illustration. Refine the lines, colors, and values to achieve the desired outcome.
- Seek Feedback and Iterate: Share your work-in-progress with others and seek constructive feedback to gain fresh perspectives. Use the feedback to refine and iterate on your illustration, improving its overall quality and impact.
Typography Design
Typography designers create and arrange typefaces, fonts, and typographic elements to enhance readability and visual appeal.
Here are some quick tips for typography design:
- Choose Appropriate Fonts: Select fonts that align with the design’s purpose, tone, and personality. Consider legibility, readability, and the intended audience when choosing fonts.
- Establish Hierarchy: Use font sizes, weights, and styles to establish a clear information hierarchy. Differentiate between headings, subheadings, and body text to guide the reader’s attention.
- Ensure Readability: Prioritize readability by selecting fonts with clear letterforms and adequate spacing. Avoid overly decorative or intricate fonts that can hinder legibility, especially at smaller sizes.
- Consider Contrast: Create contrast between different elements of the typography, such as heading and body text or important information and supporting details. Contrast can be achieved through size, weight, color, or style variations.
- Use Kerning and Tracking: Pay attention to kerning (adjusting the spacing between individual letters) and tracking (adjusting the overall spacing between letters) to ensure even and visually pleasing typography.
- Align and Balance: Maintain consistent alignment and balance within your typography design. Consider text elements’ overall layout and positioning to achieve a visually balanced composition.
- Limit Font Choices: Restrict the number of fonts used within a design to maintain visual consistency and avoid overwhelming the viewer. Limiting yourself to two or three complementary fonts is a general rule of thumb.
- Pay Attention to Line Length: Consider the optimal line length for readability. Lines that are too long or too short can make reading easier. Aim for around 45-75 characters per line, including spaces.
- Pair Fonts Thoughtfully: When combining multiple fonts, ensure they harmonize well together. Choose fonts that contrast and complement each other while maintaining a cohesive look.
- Consider Accessibility: Design with accessibility in mind by ensuring sufficient color contrast between the text and the background. This improves legibility for users with visual impairments.
Graphic Design Guide
Follow these guidelines for effective and flawless graphic design:
Understanding the Elements
- Color Theory: Learn about the psychology of colors, color harmonies, and how to effectively use colors to convey emotions and create visual impact.
- Typography: Explore the art of selecting fonts, understanding typography principles, and creating visually appealing and readable text designs.
- Layout and Composition: Discover techniques for arranging elements, balancing visual weight, establishing hierarchy, and creating engaging compositions.
- Imagery and Illustration: Understand how to choose and manipulate images, create illustrations, and integrate visuals effectively within your designs.
- Shape, Space, and Proportion: Learn how to use shapes and negative space to create visually pleasing designs and maintain proper proportions.
Applying the Principles
- Balance: Achieve visual balance by distributing elements evenly, whether it’s through symmetrical or asymmetrical arrangements.
- Contrast: Utilize contrast in colors, sizes, textures, and typography to create visual interest and make important elements stand out.
- Alignment: Establish consistent alignment to create order and cohesion in your designs. Pay attention to the placement and spacing of elements.
- Repetition: Use repetitive elements (colors, shapes, patterns, or styles) to establish consistency and reinforce visual themes throughout your design.
- Proximity: Group related elements together to create visual relationships and improve organization and readability. Elements that are connected should be visually connected.
- Hierarchy: Establish a clear hierarchy using size, color, and placement to guide the viewer’s attention and emphasize important information.
- White Space: Utilize white space strategically to create breathing room and highlight key elements. It helps improve clarity and focus within your design.
- Simplicity: Strive for simplicity by removing unnecessary elements and focusing on the core message. Keep designs clean, uncluttered, and easy to understand.
Tools and Software
- Adobe Creative Suite: Explore popular software such as Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator, and InDesign, which offer powerful tools for graphic design.
- Online Design Platforms: Discover user-friendly online platforms that provide templates, stock images, and intuitive design tools for quick and easy graphic design.
- Design Resources: Familiarise yourself with online resources for free or premium design assets, such as fonts, icons, stock photos, and textures.
Design Process and Workflow
- Research and Brief: Gather information, understand the project requirements, and research the target audience and competition.
- Concept Development: Generate ideas, create rough sketches, and explore different design directions before settling on a concept.
- Iteration and Feedback: Seek feedback from clients or peers, iterate on your designs, and refine them based on constructive criticism.
- Finalization: Prepare the final design files, ensure consistency across all elements, and export files in the appropriate formats for different purposes (print, web, etc.).
- Portfolio Building: Curate a portfolio of your best design work to showcase your skills and attract potential clients or employers.
Graphic Design Principles
These are the graphic design principles for you to follow:
- Balance: Achieving visual balance by distributing elements evenly throughout the design to create a sense of equilibrium.
- Contrast: Utilizing contrasting elements (such as color, size, or typography) to create visual interest and emphasis on specific elements.
- Alignment: Aligning elements consistently creates a sense of order and organization.
- Proximity: Grouping related elements together to create visual relationships and improve the overall organization and readability of the design.
- Repetition: Repeating design elements (such as colors, shapes, or patterns) to establish consistency and reinforce visual themes.
- Hierarchy: Establishing a clear hierarchy of elements using size, color, or placement to guide the viewer’s attention and convey importance.
- Typography: Select appropriate font sizes and spacing to enhance readability and convey the desired tone or message.
- Color: Using color effectively to evoke emotions, create visual harmony, and communicate meaning within the design.
- White Space: Incorporating white space (empty areas) gives the design room to breathe and improve clarity and focus.
- Simplicity: Striving for simplicity by removing unnecessary elements and focusing on the essential aspects of the design.
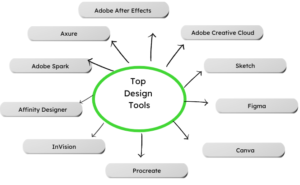
Popular Design Tools
Here are some popular design tools used by designers:

Adobe Creative Cloud:
Adobe Creative Cloud is a design software suite that includes popular tools like Adobe Photoshop, Adobe Illustrator, Adobe InDesign, Adobe XD, and more. It offers comprehensive tools for graphic design, photo editing, illustration, page layout, and user experience design.
Sketch:
Sketch is a vector-based design tool primarily used for creating user interfaces (UI) and user experience (UX) designs. It provides various features and plugins explicitly tailored for digital innovation.
Figma:
Figma is a cloud-based design and prototyping tool that allows real-time collaborative design work. It is widely used for UI/UX design, wireframing, and prototyping, with features that enable seamless collaboration and design handoff.
Canva:
Canva is a user-friendly online graphic design tool that offers a wide range of templates, fonts, and design elements. It is famous for creating social media graphics, presentations, posters, and other visual content.
Procreate:
Procreate is a digital painting and illustration app designed specifically for iPad. It provides powerful tools for creating digital artwork, illustrations, and concept designs.
InVision:
InVision is a prototyping and collaboration platform that allows designers to create interactive and animated prototypes. It facilitates collaboration between designers, developers, and stakeholders during the design process.
Affinity Designer:
Affinity Designer is a professional-grade vector graphics editor for macOS, Windows, and iPad. It offers a range of tools for graphic design, illustration, and UI/UX design, focusing on performance and precision.
- Adobe Spark: Adobe Spark is an online design tool that enables users to easily create graphics, videos, and web pages. It provides templates, themes, and intuitive editing tools for various design needs.
- Axure RP: Axure RP is a prototyping and wireframing tool that allows designers to create interactive prototypes with advanced features like conditional logic, animations, and dynamic content.
- Adobe After Effects: Adobe After Effects is a motion graphics and visual effects software widely used for creating animations, title sequences, and video effects. It offers a range of tools and products for animating and compositing visual elements.
Conclusion
If you’re looking for professional graphic design services, Noboru World is here to help. Our team of skilled designers understands the nuances of effective visual communication and can bring your ideas to life with creativity and expertise. Whether you need a captivating logo, eye-catching marketing materials, or a stunning website design, we’ve got you covered.
Contact us today at hello[at]noboruworld.com to discuss your graphic design needs. We’re passionate about delivering high-quality designs that align with your brand identity, engage your audience, and help you achieve your goals.
FAQ
What is graphic design?
Graphic design is the art and practice of combining visuals, typography, and other elements to create visual representations that convey messages or communicate ideas effectively.
What are the key skills needed for graphic design?
Key skills for graphic design include creativity, knowledge of design principles, proficiency in design software, typography, color theory, and the ability to understand and communicate visual concepts.
What is the importance of graphic design in business?
Graphic design plays a crucial role in business as it helps build brand identity, create memorable visual experiences, communicate messages effectively, and engage target audiences, ultimately contributing to business success.
What is the difference between graphic design and web design?
Graphic design primarily focuses on creating visual elements for various mediums, including print, branding, and digital media. On the other hand, web design deals explicitly with designing and structuring websites and user interfaces for online platforms.
How much does graphic design cost?
The cost of graphic design varies depending on various factors, such as the project’s complexity, scope of work, experience of the designer, and geographical location. It’s best to discuss specific requirements with a designer or agency to get a customized quote.