What is Experience Design?
“Good design is about creating a product that works well. Experience design is about creating a product that feels good.” – Jared Spool
Experience design is crucial for developing apps or websites because it ensures end-users have positive and satisfying interactions. By prioritising user needs, preferences, and emotions, experience design enhances usability, engagement, and overall user satisfaction.

Source: www.freepik.com
It helps create intuitive and seamless user journeys, improve conversion rates, and foster customer loyalty. Additionally, experience design reduces user frustration, decreases bounce rates, and enhances brand perception, ultimately leading to the app’s or website’s success and competitiveness in the digital market.
Read further to know more about design for user experience and experience design marketing.
Key Principles of Experience Design
In today’s digital landscape, creating exceptional user experiences has become of paramount importance for businesses. One crucial aspect of this is experience design.
Let us read here the fundamental principles of experience design:
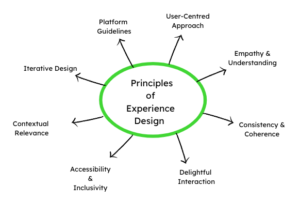
User-Centred Approach
Placing the user at the design process’s centre and focus on meeting their needs, goals, and expectations.
Let us understand why having a user centred approach for experience designing is important:
- Enhanced User Satisfaction: With the user-centred approach, the focus of designing the app is shifted towards creating a user-centric design. It will then easily align with the needs and the goals of the audience. And when you have a product like this, it will satisfy the audience better.
- Improved Usability: For high usability of the design in any app or website, user centricity helps identify the usability issues. And when the designer are involved around understanding the usability, they can optimise the design for the interface and the overall experience.
- Increased Adoption and Engagement: If you design a product with user-centric approach, your product is accepted faster. The ultimate product is designed with users in mind. And by knowing their behaviour in depth, designer get a creative and compelling design that gives higher user engagement, leading to higher adoption rates and increased user loyalty.
- Business Success: If your product is designed with high user-centricity, then it offers your business a big push. You can have a differentiated product that can keep your customers happy. It can help you differentiate your product from the competitors and build strong user relationships. This can result in increased customer loyalty, higher conversion rates, and improved business outcomes.
Empathy and Understanding
Deeply understanding the user’s perspective, motivations, and emotions to create meaningful and empathetic experiences.
Getting empathetic and understanding in experience designing:
- Insightful User Research: Understanding the users’ motivations, behaviours, and pain points requires empathetic research techniques. By empathetically engaging with users through interviews, surveys, observations, and other research methods, designers can gather valuable insights that inform the design process and help create meaningful experiences.
- Emotional Connection: Design is not solely about functionality; it also aims to evoke emotional responses from users. By empathetically understanding the target audience’s emotions, aspirations, and values, designers can craft experiences that resonate on a deeper level, fostering emotional connections and creating memorable interactions.
- Inclusive Design: Empathy is essential for designing inclusive experiences that cater to diverse user groups. By understanding the unique needs and challenges of individuals with different abilities, backgrounds, and cultures, designers can create inclusive solutions that accommodate a more comprehensive range of users, promoting accessibility and diversity.
Consistency and Coherence
Ensuring consistency in design elements, interactions, and visual language across different touchpoints to provide a cohesive and seamless experience.
Read why consistency and coherence are important in experience design:
- Reduced Cognitive Load: Consistent and coherent design reduces cognitive load for users. When design patterns and interactions remain consistent across different screens or interactions, users don’t have to learn new ways of interacting or interpreting information. This familiarity lets users focus on their tasks and goals, enhancing efficiency and reducing cognitive strain.
- Brand Identity and Trust: Consistency and coherence in design contribute to building a strong brand identity and establishing trust with users. When a product or service maintains a consistent visual style, tone of voice, and overall experience, it creates a sense of reliability and professionalism. Users are likely to trust and engage with a brand that demonstrates coherence and consistency, leading to brand loyalty and positive associations.
Contextual Relevance
Designing experiences that are relevant and tailored to the user’s context, considering factors such as device, location, environment, and user behaviour.
- Efficient and Effective Interactions: Designing with contextual relevance ensures that users are presented with the right information or features at the right time. By understanding the user’s context and anticipating their needs, designers can streamline interactions, reducing friction and cognitive load. This results in more efficient and effective user experiences.
- Enhanced User Engagement: When the experience is contextually relevant, users are likely to engage and connect with the product or service. Designers can capture and maintain user attention by providing information, content, or functionalities that are timely and meaningful in the user’s context. This increased engagement leads to a deeper and more fulfilling user experience.
Delightful Interactions
Going beyond usability to create interactions that evoke positive emotions, surprise, and delight the user, leaving a lasting impression.
- Personalization and Customization: Contextual relevance allows designers to create personalised experiences tailored to individual users. By considering the user’s context, such as location, preferences, and past interactions, designers can deliver content, recommendations, and features specifically relevant to the user’s needs and interests. This personalization enhances user satisfaction and engagement.
- Timeliness and Relevance: Designing with contextual appropriateness guarantees that information and interactions are delivered in the appropriate context and timing. By comprehending the user’s present circumstances and offering pertinent content or features, designers can enhance the user experience, rendering it more effective, practical, and significant. Users are inclined to perceive value in experiences that are timely and pertinent to their particular situation.
- Improved User Decision-Making: Contextual relevance aids users in making well-informed choices by offering them pertinent information and alternatives. When designers grasp the user’s context and supply contextual hints, they can steer users toward decisions that harmonize with their objectives and preferences. This grants users a sense of empowerment, lessens cognitive burden, and augments their decision-making process.
Accessibility and Inclusivity
Designing experiences accessible to users of diverse abilities, considering factors like colour contrast, readability, and support for assistive technologies.
- Equal Access for All: Accessibility ensures that individuals with disabilities or impairments can access and interact with products or services equally with others. By considering diverse user needs and providing inclusive design features, designers can break down barriers and ensure that everyone can participate and benefit from the experience regardless of their abilities.
- Expanded User Reach: By designing with accessibility in mind, products or services can reach a broader audience. When the experience is accessible to individuals with disabilities, it opens up opportunities for more users to engage with the product or service. This expanded user reach can lead to increased adoption, user satisfaction, and a positive impact on business outcomes.
- Ethical Responsibility: Designing inclusively is an ethical responsibility for designers. The inclusive design recognizes and respects the diversity of individuals and promotes equal opportunities. By prioritising accessibility and inclusivity, designers contribute to a more inclusive society, fostering empathy, equality, and social responsibility.
Iterative Design and Continuous Improvement
Embracing an iterative design process, gathering user feedback, and continuously refining and improving the experience based on insights and data.
- User-Centric Iteration: Iterative design allows designers to gather feedback from users early and often, enabling them to iterate and refine the design based on real user insights. By continuously involving users in the design process, designers can address usability issues, validate design decisions, and make iterative improvements that align with user needs and preferences.
- Adaptation to Changing User Needs: Ensure that you continuously improve the designs by staying connected with the market trends. By continuously gathering user feedback and monitoring user behaviour, designers can easily identify areas for improvement, implement necessary changes, and adapt the experience to meet changing user expectations.
- Enhancing Overall Quality: Continuous improvement improve the overall quality of the experience. By systematically testing, evaluating, and refining the design, designers can identify and fix usability issues, optimise interactions, and improve overall user satisfaction.
Read: What is UX Research?
The Process of Experience Design Marketing
The experience design marketing process involves a series of steps to create meaningful and impactful user experiences. Here is an overview of the typical process:
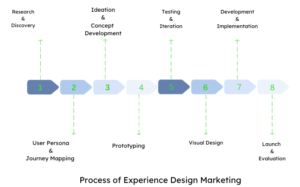
- Research and Discovery: Conduct user research to gain insights into user needs, behaviours, and preferences. This may involve user interviews, surveys, and competitor analysis to understand the target audience and the competitive landscape.
- User Persona and Journey Mapping: Creating user personas representing key user archetypes and mapping out their journeys to identify pain points, goals, and touchpoints throughout their interactions with the product or service.
- Ideation and Concept Development: Generating ideas and concepts based on user insights and requirements. This involves brainstorming sessions, sketching, and wire-framing to explore design possibilities and solutions.
- Prototyping: Designing interactive prototypes to visualize and test the suggested design concepts is known as prototyping. Before beginning development, this aids in the validation of hypotheses, gathering user feedback, and iterating on the design.
- Testing and iteration: Hold usability testing sessions with the intended audience to assess the design’s efficacy, collect feedback, and pinpoint areas for improvement. modifying the design in response to user testing’s findings.
- Visual designing: It is the process of incorporating visual elements, such as color, typography, and imagery, to improve the aesthetics and appeal of the user interface while maintaining consistency with the brand identity and user expectations.
- Development and Implementation: Working with developers to bring the design to life while making sure the user interface is accurately and optimally implemented across various platforms and devices.
- Launch and Evaluation: Releasing the product or service to the target users and monitoring its performance. Collecting user feedback, analysing metrics, and making necessary refinements to enhance the user experience further.
Collaboration, iteration, and continuous improvement are key throughout the process, allowing experienced designers to create user-centred, compelling, and engaging experiences that meet user needs and business goals.
Importance of Design for User Experience
Design plays a crucial role in shaping user experience (UX) and is essential for creating positive interactions between users and products or services. Here are key reasons why design is essential for user experience:
- User Satisfaction: Effective design gives user satisfaction by making products or services visually appealing, intuitive, and easy to use. The product then offer satisfying and enjoyable experience.
- Usability and Accessibility: Well-designed interfaces make sure that users can easily navigate, understand, and interact with the system, regardless of their technical expertise or abilities.
- Engagement and Retention: Aesthetically pleasing and engaging design encourages users to spend more time and interact more frequently with the product or service. It fosters a positive emotional connection and encourages user loyalty and retention.
- Brand Perception: Design reflects the brand’s identity and values, contributing to the overall perception of the product or service. Thoughtful and cohesive design enhances brand image, establishes credibility, and fosters user trust.
- Differentiation and Competitiveness: Design sets products or services apart from the competition in a crowded marketplace. A well-designed user experience can be a key differentiator, attracting users and gaining a competitive edge.
- Problem Solving and Efficiency: Effective design reduces frustration in users, minimises errors, and improves efficiency.
- Emotional Connection: A user friendly design can evoke emotions in the users because of the convenience and the hassle solved. By considering aesthetics, interactions, and storytelling elements, design can create a positive emotional connection, leaving a lasting impact on users.
Design shapes the user experience, influencing perceptions, behaviours, and satisfaction. By prioritising user needs, preferences, and emotions, businesses can create meaningful, engaging, and successful products or services that resonate with users and drive their success in the market.
Example of Experience Design
Apple’s products, such as the iPhone, MacBook, and Apple Watch, are renowned for their seamless and intuitive user experiences. Here’s why Apple is often praised for its experience design:
- User-Centred Approach: Apple’s design philosophy centres around the user, focusing on simplicity, ease of use, and aesthetics. Their interfaces are clean and visually appealing, with intuitive gestures and interactions that make navigating the devices a seamless experience.
- Consistency and Coherence: Apple maintains consistency across its product ecosystem, ensuring a cohesive and familiar experience for users. The design language, iconography, and interaction patterns are consistent, allowing users to effortlessly switch between devices.
- Attention to Detail: Apple pays meticulous attention to the most minor details, whether it’s the smoothness of animations, the haptic feedback, or the sound design. These details enhance the overall user experience, making it feel polished and refined.
- Delightful Interactions: Apple aims to delight users with its design choices. From the satisfying click of the home button to the animated iMessage effects, Apple incorporates subtle yet delightful interactions that create a sense of joy and surprise.
- Seamless Integration: Apple focuses on creating a seamless integration between hardware, software, and services. The design of their ecosystem allows users to effortlessly connect and sync their devices, making the overall experience more convenient and efficient.
By prioritising user needs, aesthetics, and seamless interactions, Apple has established itself as a leader in experience design. Their commitment to simplicity, consistency, and attention to detail has resulted in products delivering exceptional user experiences, earning them a loyal customer base worldwide.
Conclusion
Experience design has emerged as a critical discipline for creating successful products and services in a user-centric digital landscape. By embracing the principles of user-centeredness, empathy, consistency, and delightful interactions, businesses can elevate their offerings, foster customer loyalty, and gain a competitive edge.
By following the guidelines outlined in this comprehensive guide, you’ll be well-equipped to craft exceptional user experiences through effective experience design. Connect with us at hello[at]noboruworld.com for more insights on experience design.
FAQ
What is experience design?
Experience design creates user-centred, engaging, and meaningful experiences across various touchpoints. It involves understanding user needs, emotions, and behaviours to design products, services, and interfaces that provide a seamless and delightful user experience.
How does experience design differ from user interface (UI) design?
While UI design focuses primarily on a product or interface’s visual and interactive elements, experience design takes a broader approach. Experience design considers the entire user journey, including pre-and post-interaction phases, and aims to create a holistic and satisfying experience beyond just the interface itself.
Why is experience design important?
Experience design is essential because it directly impacts user satisfaction, engagement, and loyalty. By creating intuitive, aesthetically pleasing, and emotionally engaging experiences, businesses can differentiate themselves, foster customer loyalty, and gain a competitive edge in the market.
How does experience design benefit businesses?
Experience design benefits businesses by enhancing customer satisfaction, increasing user engagement, and driving brand loyalty. By focusing on user needs and emotions, businesses can create experiences that resonate with their target audience, resulting in higher customer retention, positive word-of-mouth, and, ultimately, business growth.
How can businesses incorporate experience design into their processes?
Businesses can incorporate experience design by adopting a user-centric approach, conducting user research and testing, mapping user journeys, and involving multidisciplinary teams. By integrating experience design principles and methods into their development processes, businesses can create products and services that meet user expectations and deliver exceptional experiences.



