Random Sampling
Definition
Random sampling is a statistical method of selecting a subset of individuals or items from a larger population in which each member has an equal chance of being chosen.
Description
It is a statistical technique to select a representative subset of individuals or items from a larger population. This method involves selecting individuals or items randomly, which means each member of the population has an equal chance of being selected for the sample.
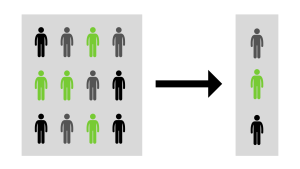
By selecting a sample randomly, the sample is more likely to be representative of the population, and the results obtained from the sample can be generalised to the larger population with greater confidence. It is widely used in research and data analysis to make inferences about a population based on a sample.
Importance of Random Sampling
- Helps to ensure that the sample selected is representative of the larger population.
- Reduces the chances of bias in the sample selection process.
- Increases the chances of obtaining accurate and reliable results.
- Allows for generalisations to be made about the population based on the sample.
- Helps to reduce the cost and time required for data collection by selecting a smaller subset of individuals or items.
- It is widely used in research and data analysis across various fields and industries.
- Provides a basis for statistical inference and hypothesis testing.
- It can help to identify patterns and relationships within the data.
- Helps to improve the validity and reliability of research studies.
- Is essential for ensuring that research findings can be applied to real-world situations.
How to prepare for Random Sampling?
These are the steps to prepare for random sampling:
- Define the population: Clearly define the people you want to study. This will help you determine the sample size you need to select.
- Determine the sample size: Based on the size of the population, determine the sample size you need to select. This can be done using statistical formulas or software.
- Choose a method: There are several methods, including simple random sampling, stratified random sampling, and cluster sampling. Choose the method that is most appropriate for your research study.
- Select the sample: Once you have chosen a method, select the sample using a random number generator or other software. Ensure that each member of the population has an equal chance of being selected.
- Validate the sample: Validate the sample to ensure that it is representative of the larger population. Check for any biases or anomalies that may have affected the sample selection process.
- Analyse the data: Analyse the data obtained from the sample and draw conclusions about the larger population. Use statistical tools to make inferences and generalise the findings to the population.
Future Scope of Random Sampling
It will continue to be an essential statistical method in the future for a variety of reasons:
- It helps to ensure that the sample selected is representative of the larger population, which is essential for making accurate and reliable inferences about the people.
- As data becomes more complex and the number of variables increases, it can reduce the cost and time required for data collection by selecting a smaller subset of individuals or items.
- It can reduce bias in the sample selection process, which is important for ensuring that external factors do not influence the results.
- With the rise of big data and machine learning, it can be used to improve the performance of algorithms by selecting a representative subset of data for training and testing.
- It can also be used in quality control and assurance to ensure that products or services meet the standards set by the larger population.
Example
A brand example of random sampling could be a company that produces a new type of energy drink and wants to know how it is received by consumers. The company could use it to select a representative sample of individuals from the larger population of potential consumers to try the energy drink and provide feedback.
The company could use a simple random sampling method to randomly select individuals from a list of potential consumers or use stratified random sampling to select individuals from different demographics such as age, gender, and location.
FAQ
What is random sampling?
It is a statistical technique to select a representative subset of individuals or items from a larger population. This method involves selecting individuals or entities randomly, which means each member of the population has an equal chance of being selected for the sample.
Why is random sampling necessary?
Random selection is important because it helps to ensure that the sample selected is representative of the larger population, which is essential for making accurate and reliable inferences about the people. By selecting individuals or items randomly, each member of the population has an equal chance of being selected for the sample, which helps to avoid bias and increases the chances of obtaining accurate and reliable results.
What are the different types of random sampling methods?
There are several types of random sampling methods, including simple random sampling, stratified random sampling, and cluster sampling.
How do you select a sample using random sampling?
You can use a random number generator or other software to select a sample using it. Ensure that each member of the population has an equal chance of being selected.
What is the sample size in random sampling?
It is the number of individuals or items selected for the sample. The size of the sample depends on the size of the population and the level of precision required for the study.
Can random sampling be used in qualitative research?
Yes, a random sample can be used in qualitative research, although it is more commonly used in quantitative analysis. In qualitative research, it can be used to select a representative sample of individuals for interviews or focus groups.
How can you validate the sample in random sampling?
To validate the sample, you can check for any biases or anomalies that may have affected the sample selection process. You can also compare the characteristics of the sample to the larger population to ensure that it represents the people.
What are the limitations of random sampling?
The limitations include the potential for sampling error, which can occur when the sample is not representative of the larger population. Additionally, random selection may not be appropriate for specific populations or research questions.





We would love to have your opinion.