Staff Augmentation Vs Outsourcing: Which Model Should You Choose?
Did you know Apple outsources the manufacturing of its products, such as iPhones and MacBooks, to companies like Foxconn and Pegatron?
Because of this, Apple focuses on design, innovation, and marketing while leveraging the manufacturing expertise of its partners.
Similarly, Microsoft often utilises staff augmentation by hiring temporary software developers and engineers to work on specific projects, such as developing a new version of Windows or a software update.
This approach helps Microsoft quickly scale its workforce to meet project demands without the long-term commitment of hiring full-time employees.
If you are looking for skilled manpower to get that project completed, you can contact us. And before that read further to understand what will satisfy your demands.
What is Staff Augmentation?
Staff Augmentation is a business strategy in which an organisation augments or supplements its existing workforce by hiring temporary professionals, often contracted to address specific project needs or skill gaps.
These temporary staff members, augmented staff or consultants, work alongside the in-house team to contribute their expertise and help achieve project goals. Staff augmentation provides flexibility, scalability, and access to specialised skills without the long-term commitment of hiring full-time employees.
It allows organisations to adapt to changing workloads and project requirements efficiently.
Benefits of Staff Augmentation
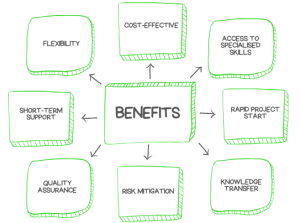
Here are the detailed benefits of staff augmentation:
1. Flexibility:
Staff augmentation provides the flexibility to quickly scale your workforce up or down based on project needs and changing workloads. You can easily add or remove temporary staff members as required, allowing for efficient resource allocation.
2. Cost-Effective:
It can be more cost-effective than hiring full-time employees, as you only pay for augmented staff services when needed. You can avoid the overhead costs associated with permanent hiring, such as benefits, training, and long-term commitments.
3. Access to Specialised Skills:
Staff augmentation allows you to tap into a pool of specialised professionals with specific skills or expertise that your in-house team may lack. This is particularly valuable for short-term projects requiring niche knowledge.
4. Rapid Project Start:
With staff augmentation, you can quickly assemble a project team without the time-consuming process of hiring full-time employees. This accelerates project initiation and completion.
5. Reduced Workload for Existing Staff:
Augmented staff members can help alleviate the workload of your existing team, preventing burnout and maintaining productivity. This is especially beneficial during peak work periods or when facing resource shortages.
6. Knowledge Transfer:
Augmented staff members can share their expertise with your in-house team, fostering knowledge transfer and skill development within your organisation. This can lead to long-term improvements in your team’s capabilities.
7. Risk Mitigation:
Staff augmentation can reduce the risk associated with hiring full-time employees, especially in uncertain economic environments. You have the flexibility to adapt to changing circumstances without making permanent commitments.
8. Enhanced Focus on Core Competencies:
With temporary staff handling specific tasks or projects, your core team can concentrate on strategic initiatives and core business functions, improving overall efficiency and competitiveness.
9. Quality Assurance:
Augmented staff members are typically selected based on expertise and experience. This can result in improved project quality and reduced errors compared to relying solely on your existing team.
10. Scalability:
Staff augmentation enables you to respond swiftly to unexpected opportunities or challenges, ensuring you have the necessary workforce to capitalise on market changes or address emerging needs.
11. Short-Term Support:
It’s ideal for short-term projects or initiatives where hiring permanent employees may not be justified. You can tailor the duration of staff augmentation to the project’s specific requirements.
12. Geographic Reach:
You can access talent from various geographic locations, allowing for a diverse team and potential cost savings based on regional differences in labour costs.
Drawbacks of Staff Augmentation
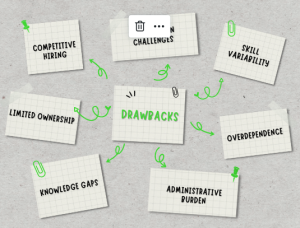
Staff augmentation remains valuable when used strategically and complemented with effective management practices. Organisations can address many challenges through careful planning, communication, and ongoing performance management of augmented staff.
1. Integration Challenges:
Augmented staff may need help integrating into the existing team, leading to potential communication and collaboration issues. Cultural differences and varying work styles can hinder teamwork.
2. Short-Term Commitment:
While flexibility is a benefit, it can also be a drawback. Temporary staff may have a different level of commitment or loyalty than full-time employees, which could affect their dedication to the project or organisation.
3. Skill Variability:
The quality of augmented staff can vary, and it’s possible to encounter individuals with skills that do not match their claims. Proper vetting and selection are essential to mitigate this risk.
4. Limited Cultural Alignment:
Temporary staff may need to fully understand or align with the company’s culture and values, potentially leading to a lack of engagement or enthusiasm for the organisation’s goals.
5. Overdependence:
Relying too heavily on staff augmentation can lead to overdependence on external talent, which may lead to a lack of investment in developing in-house skills and expertise.
6. Data Security Concerns:
Augmented staff may access sensitive company data, raising concerns about data security and confidentiality breaches. Proper data protection measures are crucial.
7. Training and Onboarding:
Incorporating temporary staff into projects may require time and resources for training and onboarding, which can impact project timelines and budgets.
8. Administrative Burden:
Managing augmented staff, contracts, payments, and performance evaluations can add administrative complexity to the HR and project management processes.
9. Knowledge Gaps:
Temporary staff may need a deeper understanding of the company’s products, services, or long-term strategies, which could limit their ability to make informed decisions.
10. Limited Ownership:
Augmented staff may feel they need more ownership or responsibility for the organisation’s long-term success, potentially leading to a lack of commitment to achieving organisational objectives.
11. Uncertainty for Augmented Staff:
Temporary employees may face job insecurity, as their contracts may not guarantee long-term employment. This can affect their job satisfaction and morale.
12. Competitive Hiring:
In some industries or regions, finding and hiring skilled augmented staff can be competitive, leading to potential delays in project start times.
What is Outsourcing?
Outsourcing is a business practice in which an organisation contracts specific tasks, processes, or functions to external third-party companies or service providers.
These external entities, often located domestically or overseas, assume responsibility for performing the outsourced tasks or providing the specified services. Outsourcing is commonly employed to reduce costs, access specialised expertise, enhance efficiency, and enable organisations to focus on their core competencies.
It allows businesses to delegate non-core functions, such as customer support, IT services, or manufacturing, to external partners, freeing up internal resources and streamlining operations.
Benefits of Outsourcing
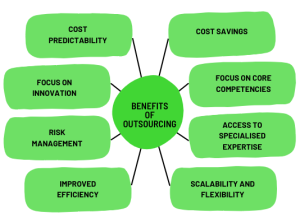
Outsourcing can be a strategic approach that offers numerous benefits, enabling organisations to become more efficient, competitive, and adaptable in a global marketplace.
Here are the benefits of outsourcing:
1. Cost Savings:
Outsourcing allows businesses to reduce operational costs significantly. Companies can access skilled labour in countries with lower labour costs, avoiding the expenses associated with hiring and training in-house employees.
2. Focus on Core Competencies:
Outsourcing non-core functions enables organisations to concentrate on their core activities and strategic objectives. This enhances overall efficiency and productivity.
3. Access to Specialised Expertise:
Outsourcing providers often specialise in specific areas. They provide access to specialised skills and knowledge that may only be available in some places.
4. Scalability and Flexibility:
Outsourcing provides scalability, allowing businesses to quickly adjust resources up or down based on changing demands without the challenges of hiring or downsizing internal teams.
5. Improved Efficiency:
You ultimately lead to improved efficiency and quality of work as your outsourcing partners are typically experts in their fields. This results in faster project completion and better outcomes.
6. Risk Management:
Shared responsibilities and risks with outsourcing partners can provide risk management, mainly when dealing with complex projects or compliance issues.
7. Time Savings:
When you outsource your tasks, you can save valuable time, as external experts can often complete work more efficiently and quickly, freeing up internal resources for other priorities.
8. Access to Advanced Technology:
Outsourcing providers frequently invest in the latest technology and tools. It allows businesses to benefit from cutting-edge solutions without the upfront investment.
9. Focus on Innovation:
Internal teams can allocate more time and resources to innovation, research, and development, leading to product and service improvements if a crucial part of the project is outsourced.
10. Global Reach:
Outsourcing enables businesses to tap into a global talent pool and expand their operations or services to international markets more easily.
11. Cost Predictability:
Understand that outsourcing agreements often involve fixed costs or predictable pricing models, making budgeting and financial planning more manageable.
12. Competitive Advantage:
When you outsource, you get a competitive edge by helping businesses adapt quickly to market changes, launch products faster, and stay agile in a rapidly evolving business environment.
13. Compliance and Regulations:
Outsourcing providers often have expertise in handling regulatory compliance, reducing the risk of legal issues and penalties.
14. Reduced Overhead:
Outsourcing eliminates the need for additional office space, equipment, and infrastructure, reducing overhead costs.
15. 24/7 Operations:
Some outsourcing providers offer round-the-clock support, allowing businesses to serve customers or address issues anytime.
Major Drawbacks of Outsourcing
Here are five significant drawbacks of outsourcing:
1. Loss of Control:
When tasks or processes are outsourced, businesses may have less direct control over how those activities are performed. This can lead to concerns about quality, adherence to standards, and communication gaps.
2. Quality Concerns:
Depending on the outsourcing partner’s capabilities and commitment to quality, there may be issues with the quality of work delivered. Differences in standards and expectations can also pose challenges.
3. Security and Confidentiality Risks:
Sharing sensitive data or confidential information with outsourcing providers can expose businesses to data breaches, security risks, and breaches of confidentiality agreements.
4. Cultural and Language Barriers:
Outsourcing to international providers may result in language barriers and cultural differences that hinder effective communication and collaboration.
5. Hidden Costs:
While outsourcing can save costs in many cases, there may be hidden or unexpected costs, such as legal fees, transition expenses, or management overhead, that businesses must consider.
Difference between Staff augmentation Vs Outsourcing
These are the major differences between staff augmentation Vs outsourcing:
| Aspect | Staff Augmentation | Outsourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Temporary addition of external resources to complement the in-house team. | Contracting out specific tasks or functions to external third-party providers. |
| Team Management | Augmented staff work alongside the existing in-house team, managed by the organisation. | Outsourcing providers work independently or semi-independently, managed by the service provider. |
| Control | The organisation retains control over the project, tasks, and management of augmented staff. | The service provider typically has more control over the outsourced tasks or processes. |
| Integration | Augmented staff are integrated into the organisation’s existing workflow and culture. | Outsourcing may involve less integration, potentially leading to cultural and communication challenges. |
| Expertise | Augmented staff bring specific skills and expertise to complement the existing team. | Outsourcing providers offer specialised skills and knowledge in specific areas. |
| Project Duration | Typically used for short-term projects or to address temporary skill gaps. | Can be used for both short-term and long-term projects, as well as ongoing services. |
| Flexibility | Offers flexibility to scale up or down quickly based on project needs. | Provides flexibility in scaling resources, but may involve longer setup times. |
| Cost Control | Costs are often more predictable, as augmented staff are paid for the duration of their contracts. | Costs can vary depending on the service provider’s pricing model and project scope. |
| Core Competency Focus | Allows the organisation to maintain focus on core competencies while addressing specific needs. | Enables the organisation to delegate non-core functions, allowing a more specialised focus. |
| Risk Distribution | The organisation shares risks and responsibilities with augmented staff. | The service provider assumes a significant portion of the risks and responsibilities. |
| Communication | Communication with augmented staff is usually direct and managed by the organisation. | Communication with outsourcing providers is often facilitated through a designated contact person or team. |
| Data Security | Data security is typically managed in-house, with control over sensitive information. | Data security may be a shared responsibility, potentially leading to concerns about confidentiality. |
Also Read : Hiring Inhouse team Vs Outsourcing
Conclusion
The choice between outsourcing and staff augmentation isn’t one-size-fits-all; it’s about aligning your strategy with your unique objectives. Outsourcing offers long-term efficiency and specialisation, while staff augmentation brings adaptability for evolving needs.
As you navigate this decision, consider your project’s scope, budget, and timeline. For expert guidance and support in implementing your strategy, contact Noboru at hello[at]noboruworld.com. Your journey to optimise your workforce begins with a tailored approach that fits your organisation.
FAQ
1. What’s the primary difference between staff augmentation and outsourcing?
In staff augmentation, external professionals are temporarily added to your existing in-house team to complement their skills or address specific project needs. The augmented staff works under your organisation’s management.
Outsourcing involves contracting out specific tasks or functions to external third-party providers who operate independently or semi-independently. The service provider takes responsibility for completing the outsourced work.
2. How do I decide whether to opt for staff augmentation or outsourcing for a project?
The choice depends on your project’s scope, duration, and goals. Staff augmentation suits short-term needs or skill gaps within your team, while outsourcing is ideal for long-term projects or when you need comprehensive external solutions.
3. What are the risks associated with both staff augmentation and outsourcing?
Staff Augmentation Risks: Integration challenges, variable quality of augmented staff, cultural differences, and concerns about data security.
Outsourcing Risks: Loss of control, quality concerns, security and confidentiality risks, cultural and language barriers, and potential hidden costs.
4. How can I ensure successful staff augmentation or outsourcing partnerships?
To ensure success, establish clear communication channels, define project expectations, vet and select reliable partners, and have well-documented contracts.
Ongoing performance management and a collaborative approach are also crucial for both models.



