Google Core Web Vitals: What Is It and How It Can Impact SEO?
Introduction
In the recent update that rolled out in 2022, Google mentioned that making page experience an essential factor for ranking is vital.
The site owners can get on to the job of improving their page experience using the Google Search Console Report. And when they do it, the ranking will automatically get better.
The Core Web Vitals define the metrics for Google’s Page experience that quantify the user experience of interacting with the page. For example, it tells about how fast the page is visible, about the visual stability, and how long it takes before a user can interact with the page.
Core Web Vitals matter significantly if you talk about page ranking and improved SEO.
Let us read in detail what are core web vitals and how it affects SEO.
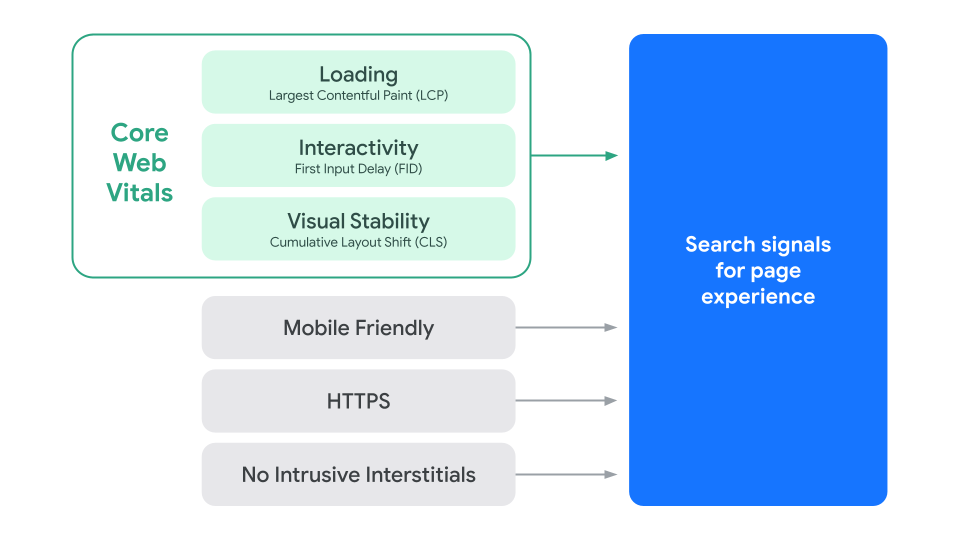
What are Core Web Vitals?
Source: https://developers.google.com
Core Web Vitals are a set of performance metrics that quantify the user’s experience. Google developed this tool to measure the experience on a web page.
If you are looking to have an increased impact on Google, working on Core Web Vitals is essential. Page experience has become a core ranking factor that drives organic traffic to your web page. The algorithm would surround these to categorise the page performance according to the three metrics:
→ Safe browsing.
→ Website address includes HTTPS
→ Mobile friendliness
→Content accessibility without many pop-ups
Next, you can read the three metrics that define the Core Web Vitals of a page:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
- First Input Display (FID)
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
Let us look at each component separately in detail:
Largest Contentful Paint
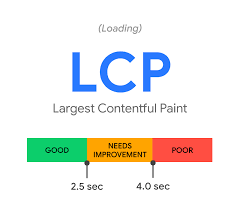
Largest Contentful Pain is a metric that measures the load time. To be precise, it measures the largest time that it takes to display the content element within the viewable area of the user’s screen.
The metric does not measure the entire page. Some of the essential elements that affect the load time of the page include:
- Featured image
- Blocks of text
- <img> element
- H1
- The image inside a video
- The background image is loaded with the URL () function.
According to Google, a website having an LCP of 2.5 seconds or less is said to be suitable for user experience. However, anytime more than this is taken can deteriorate the experience and result in an increased bounce rate.
Thinking about how you can make the LCP of a webpage better?
Here are a few steps to bear in mind when you are bothered by LCP:
- Upgrade to a faster web host
- Cache assets
- Remove unnecessary third-party scripts
- Remove page elements that take more time to load the page
- Minify the CSS
- Install a CDN
Another metric to look at is First Input Display (FID).
First Input Display (FID)
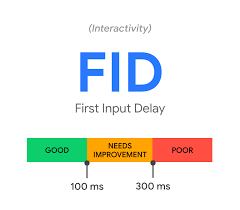
FID is a core web vital metric that measures the time of interaction, that is, the difference between the time when the user gives an input, and the page responds.
The input from a user can be clicking, tapping, etc. For example, you can say how responsive a page is. If a web page takes more time to load and display the information, the user will get frustrated and leave the page.
According to Google, an FID of 100 milliseconds or less is most suitable.
These are the ways you can improve the FID:
- Minimise the JavaScript; otherwise, it interferes with the site when JS is running.
- Remove less essential third-party scripts.
- Browser caching can store elements and save time when the website loads.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
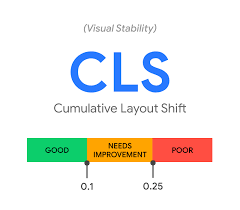
Cumulative Layout Shift is another relevant metric that measures the visual stability of the page. It indicates the proportion of the screen that shifts and how far the elements move.
Unexpected layout shifts can be frustrating for the users forcing them to leave the page as soon as possible. CLS is calculated by :
CLS= Impact fraction X Distance Fraction
→Impact fraction is the percentage of viewports that shifts.
→Distance Fraction is movement distance divided by the height of the viewport.
According to Google, a CLS score of 0.1 or less is good. The desktop or the mobile version has to hit the score about 75% of the time.
You can improve your CLS with these:
- Control the ads so that they do not appear suddenly.
- Do not install too many pop-ups or banners that cause shifts in the screen layout.
- Use images and videos of standard dimensions.
How can Core Web Vitals impact your SEO?
Core Web Vitals are important metrics that give you an idea of what experience your web page offers for your website. In addition, the data metric gives an idea to the owner of how they can improve the web page’s functionality, making it rank higher on the search engine.
- With CLS, FID, and LCP, the website owner can identify which metric they have to improve.
- The more satisfied users your web page gets, the more likely it is that they will return for a visit. It improves the chances of ranking higher.
- Core Web Vitals contribute to bringing organic traffic and increasing the ranking.
- With better Core Web Vitals, you get more engaged customers and comparatively higher conversion rates, which leads to higher revenues.
Page experience is the ultimate factor and not anything else. If the page takes more time to load, no matter how much high-quality content it has, the chances of ranking fail.
Next, let us look at the tools that you can use to measure the Core Web Vitals.
Tools to measure the Core Web Vitals
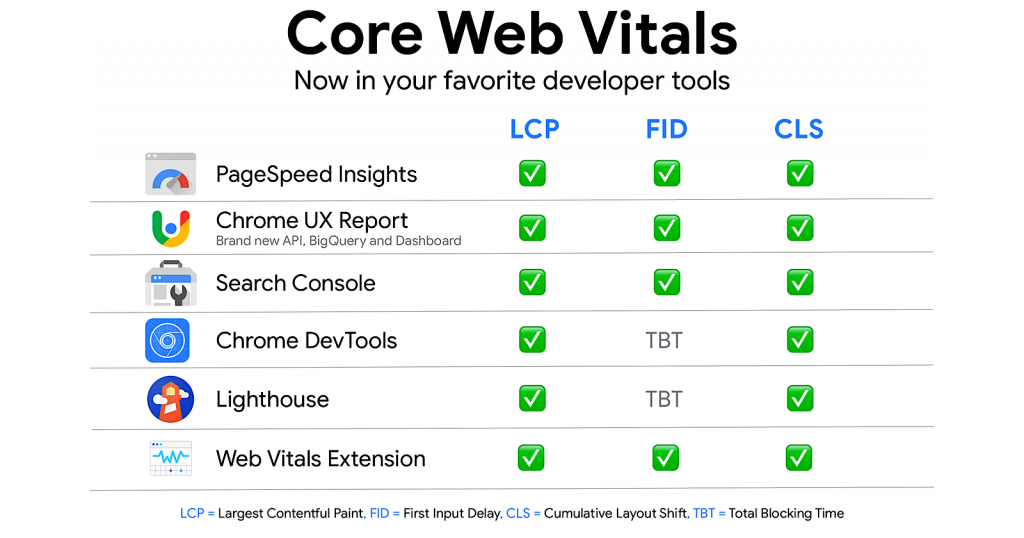
Some of the tools to measure the Core Web Vitals include:
- Search Console:
- The Google Search Console has a new extension to generate Core Web Vitals reports.
- It indicates pages that need urgent attention based on real-world data.
- If a url does not have a minimum data, the reports will be omitted.
- You can access the tool here.
- CrUX
- CrUX gives a report that is based on the dataset of the real user experience.
- The tool measures the web pages in terms of loading and interaction with it. This is commonly known as Real User Monitoring (RUM).
- CrUX has a fast API that can be easily integrated to measure in the metrics to include LCP, CLS, FID and First Content Paint (FCP).
- You can access the tool here.
- Chrome DevTools
- The Chrome DevTools has a new panel that helps you evaluate unexpected layout shifts.
- You can use the tool to debug the total blocking time (TBT).
- TBT gives the difference between First Contentful Paint and Time to Interactive (TTI), that is, the time to prevent input responsiveness.
- You can explore the tool here and use it to improve your page ranking.
- Lighthouse
- Lighthouse is an automated tool that helps the developers to identify the issues and fix them to improve the user experience.
- The latest version of Lighthouse 6.0 works on the three metrics to include Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS), and Total Blocking Time (TBT).
- You can read about the tool here.
- Page Insights Speed
- Page Insights Speed reflects the performance of a web page on both mobile and desktop services.
- The tool defines how the users experience the page.
- The reports suggest how to improve the page’s performance, accessibility, and SEO. Read more about the tool here.
Conclusion
Core Web Vitals are the important ranking factor that occupied a place more relevant just like other tools that drive organic traffic.
If you are looking for solutions to improve the page experience for the users and hence the ranking, you can contact us. You can also write to us hello[at]noboruworld.com.





We would love to have your opinion.